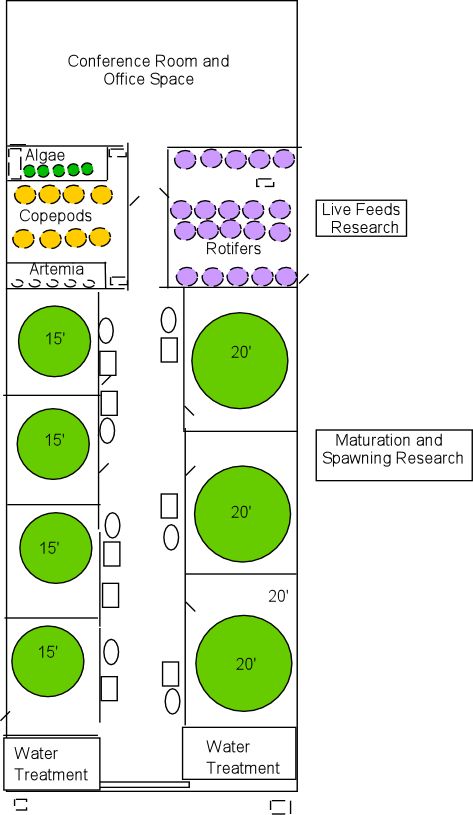
Building Diagram
 |
The
Center for Aquaculture Research and Development is constructing new facilities
at Mote Aquaculture Park (MAP) to replace the aquaculture research facilities
located at the main campus on
Live Feeds Research The Live Feeds Research laboratories are still under
construction. This facility will contain separate rooms for growing the algae,
brine shrimp, rotifers, copepods and other live feeds. The algal culture
laboratory construction is nearly complete. Due to the demand for
high-salinity seawater in the production of live feeds, construction of the
other live feeds laboratories will continue when the seawater filtration
systems are completed. Algae Room
The
Live Feeds Research laboratories will provide the food needed to culture fish,
shrimp and queen conch. Marine fish larvae are typically much smaller than
freshwater fish larvae and require very small live prey. Live feeds for marine
fish larvae can range in size from 30 to over 500 micrometers in size (1
micrometer = 0.0000394 inches). Copepods and rotifers are the generally
accepted as the first food for these fish larvae. As the fish grow, they are
fed larger live feeds, including newly hatched brine shrimp (Artemia).
Maturation and Spawning Research The Maturation and Spawning Research facility includes three 20-foot diameter tanks (14,348 gallons or 54,315 liters per tank) and four 15-foot diameter tanks (6,700 gallons or 25,320 liters per tank). Each system has independent light and temperature controls to simulate specific seasonal conditions. By manipulating these conditions, the marine fish broodstock can potentially be acclimated to spawn for longer periods of time and during periods that wild fish do not normally spawn. Marine broodstock are routinely monitored for weight, length, and gonadal development. Eggs collected from these broodfish will later be stocked into tanks contained in the Marine Hatchery and Nursery facility.
|
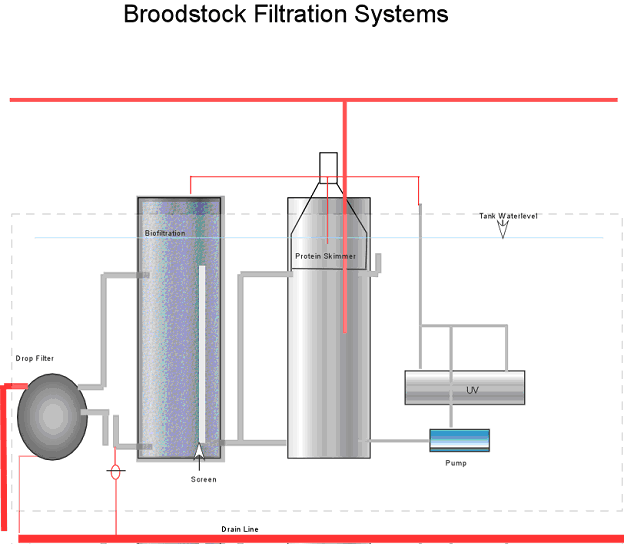 |
Broodstock
Primary Filtration System (Actual photo)  |
Broodstock
Secondary Filtration System |
(Diagram from above) 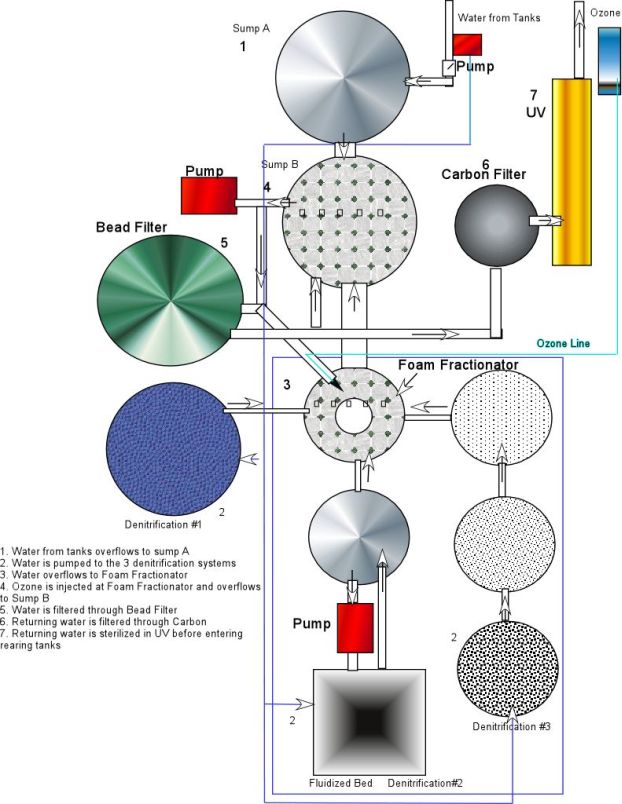 |


